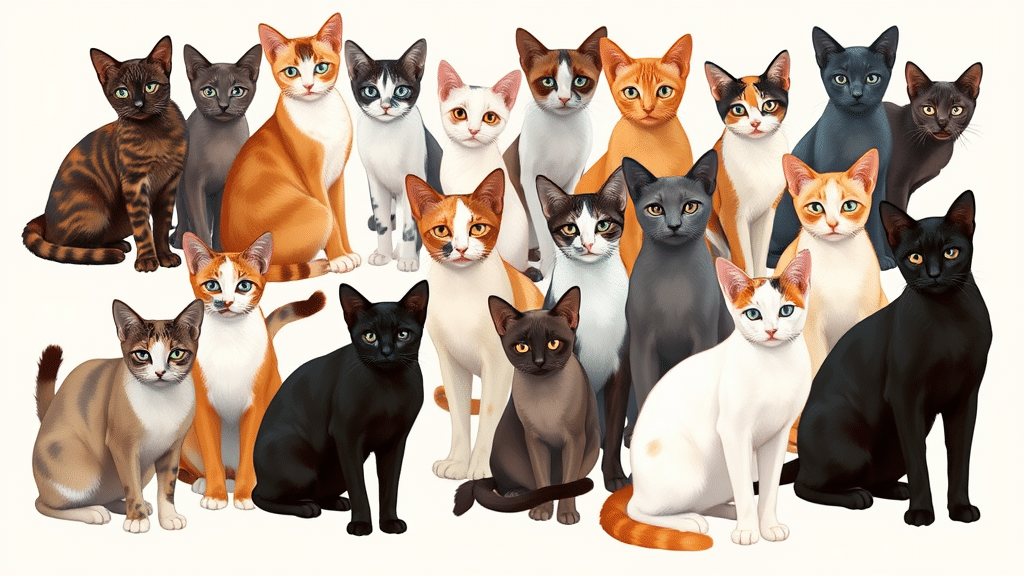
Manx cats come in many different colors and patterns, making each one unique.
The color range includes solid colors, tabby patterns, tortoiseshell, calico, and bicolor combinations.
These color variations help cat owners tell their pets apart and give each Manx its own look.
For breeders, coat colors are important markers that help track genetic traits across generations and plan thoughtful breeding programs.
The right color combinations can highlight the Manx’s special traits – like their rounded body shape and the lack of a tail that makes this breed so well-known.
Common Manx Cat Colors
Tabby Manx Cats
Tabby Manx cats come in mackerel (thin stripes), classic (swirling patterns), and spotted varieties.
All tabbies have the signature “M” mark on their forehead.
These patterns are caused by dominant genes, making them very common in the Manx breed.
Tortoiseshell Manx Cats
Tortoiseshell Manx cats have black and red colors mixed together in a mottled pattern.
Each tortie has a unique pattern.
They’re almost always female because the black and red colors are linked to the X chromosome, and females have two X chromosomes.
Calico Manx Cats
Calico Manx cats have white patches plus black and red colors.
Unlike tortoiseshells, where colors blend together, calicos show three distinct colors.
Like torties, calicos are almost always female due to the X-linked color genes.
Solid Color Manx Cats
Solid Manx cats come in one color throughout their coat.
Common colors include black, blue (gray), red (orange), and cream.
These solid colors highlight the Manx’s round body shape and strong build since no patterns distract the eye.
Rare Manx Cat Colors
Color-Pointed Manx Cats
Color-pointed Manx cats have darker colors on their face, ears, paws, and tail area, with a lighter body color. This pattern makes them look different from typical Manx cats.
The color-point pattern in Manx cats came from crossing with Siamese or Himalayan breeds.
The gene that causes this pattern is heat-sensitive, making the cooler parts of the body (extremities) darker.
Color points can appear in many shades, including seal, blue, chocolate, and lilac.
Smoke-Coated Manx Cats
A smoke coat looks solid at first glance, but each hair has a white or silver base that shows when the cat moves.
This creates a striking effect where the coat changes color as the catwalks.
To spot a blue or black smoke Manx, look at the fur when the cat is in motion. The outer coat will be dark (blue or black), but a lighter undercoat will flash through.
Running your hand against the fur’s growth will also reveal the lighter roots.
Smoke Manx cats often have a silver ruff around their neck where the contrast between dark tips and light roots is most visible.
Manx Cat Coat Patterns & Combinations
Bi-Color Manx Cats
Bi-color Manx cats show a mix of white and other colors. Popular combinations include black and white (tuxedo), blue and white, and red and white.
These cats might have white on their chest, paws, belly, or face.
The white areas in bi-color Manx cats result from the white spotting gene, which prevents color from forming in certain body parts.
The amount of white can vary widely. Some cats have a small white patch on the chest, while others may be mostly white with color only on the head and tail.
The location and size of white patches differ with each cat, creating many possible patterns.
Tri-Color Manx Cats
Tri-color Manx cats show three colors: white, black, and red (orange). This group includes calico cats (large patches of the three colors) and tortie-and-white cats (mixed black and red with white patches).
The genetics for tri-colors is complex. Like tortoiseshell cats, they need two X chromosomes to show black and red colors, making most tri-colors female.
The white spotting gene adds the third color.
The amount of each color varies from cat to cat, with some showing mostly white with small patches of color, while others might have larger colored areas with less white.
Striped & Spotted Manx Cats
Tabby Manx cats show stripes or spots due to the agouti gene. This gene creates bands of color on each hair, resulting in the tabby pattern.
The agouti gene works with other color genes to create different tabby types.
In mackerel tabbies, it forms thin stripes; in classic tabbies, it creates swirls; and in spotted tabbies, it breaks the stripes into dots.
All tabby Manx cats have the same basic pattern elements: the “M” mark on the forehead, stripes on the face, and ringed patterns on the legs and tail area.
The clarity of these patterns can change based on the cat’s base color, with patterns showing more clearly on lighter-colored cats.
Do Manx Cat Colors Affect Their Personality?
Theories and Myths About Coat Color and Temperament
Many cat owners think certain colors indicate specific personality traits in Manx cats.
Orange cats are often thought to be friendlier, while black cats are seen as more independent.
These ideas come from folk wisdom and personal stories rather than facts.
Some Isle of Man traditions link coat patterns to behaviors, but these are mainly cultural stories with little basis in science.
Research and Anecdotal Evidence
Scientific studies show no strong connection between coat color and cat personality.
A Manx cat’s temperament comes mostly from genetics, early life experiences, and how they were raised.
Breed traits matter more than color – Manx cats typically show playfulness, intelligence, and loyalty regardless of their coat color.
Most cat experts suggest looking at each cat as an individual rather than making choices based on color myths.
The Genetics Behind Manx Cat Colors
Coat colors in Manx cats pass from parents to kittens through specific genes.
Each kitten gets one set of color genes from each parent, which combine to create the kitten’s final color.
This explains why a litter can have kittens with different colors even with the same parents.
Some color genes are stronger (dominant), while others are weaker (recessive).
Dominant genes show up whenever they’re present, even if paired with a different gene.
For example, the gene for black color is dominant over red. Recessive genes only show when a cat has two copies of that gene.
The gene for dilute colors (like blue instead of black or cream instead of red) is recessive, which is why these colors are less common.
The genes for color in Manx cats work the same way they do in other cat breeds.
What makes Manx cats special is the combination of these color genes with the gene that causes their tailless trait.
The main genes that control color work independently from the Manx gene so that Manx cats can come in the same wide range of colors as other cats.
Conclusion
Manx cats show an amazing range of coat colors and patterns, from basic solids and tabbies to the more unusual color points and smoke coats.
The mix of genetics creates many coat colors, each making the Manx’s strong body shape and tail-free form stand out.
While some colors, like tortoiseshell and calico, link to female cats due to their X-chromosome connection, others, like tabbies, appear across both sexes.
The blend of these color genes with the Manx gene results in visually stunning and genetically fascinating cats.
Comment your favorite!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Manx Cat be Orange?
Yes, Manx cats can be orange. This color, red or ginger, is common in the breed and can appear in solid, tabby, or mixed patterns.
What is the Rarest Manx Cat Color?
Solid blue is among the least common Manx cat colors. True all-white Manx cats with blue eyes are rare and highly valued.
Do Manx Cats Change Color as They Grow?
Manx kittens may show slight color changes as they mature. Their coat patterns often become more clear and defined as they reach adulthood.